
| Volume (g) | |||||
| Smokers | 621 | 793 | 593 | 545 | 753 |
| 655 | 895 | 761 | 714 | 598 | |
| Non-smokers | 947 | 945 | 1083 | 1202 | 973 |
| 981 | 930 | 745 | 903 | 899 | |
You can create parallel boxplots of the two samples with the commands Here are parallel boxplots of the samples:
The summary statistics are obtained with They are| Sample | Sample | ||
| n | mean | SD | |
| Smokers | 10 | 692.8 | 109.0492 |
| Non-smokers | 10 | 960.8 | 119.6224 |
Estimated difference in means
| SE | 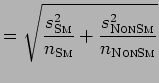 |
|
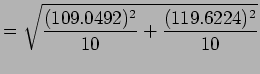 |
||
Welch Two Sample t-test
data: smokers and nonsmokers
t = -5.2357, df = 17.848, p-value = 2.872e-05
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is less than 0
95 percent confidence interval:
NA -179.1973
is computed by
We can also obtain a confidence interval for the difference between
the mean volumes for smokers and non-smokers:
Welch Two Sample t-test
data: smokers and nonsmokers
t = -5.2357, df = 17.848, p-value = 5.743e-05
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-375.6059 -160.3941
sample estimates:
mean of x mean of y
692.8 960.8
Try some examples of your own in the work area below.
